Articles
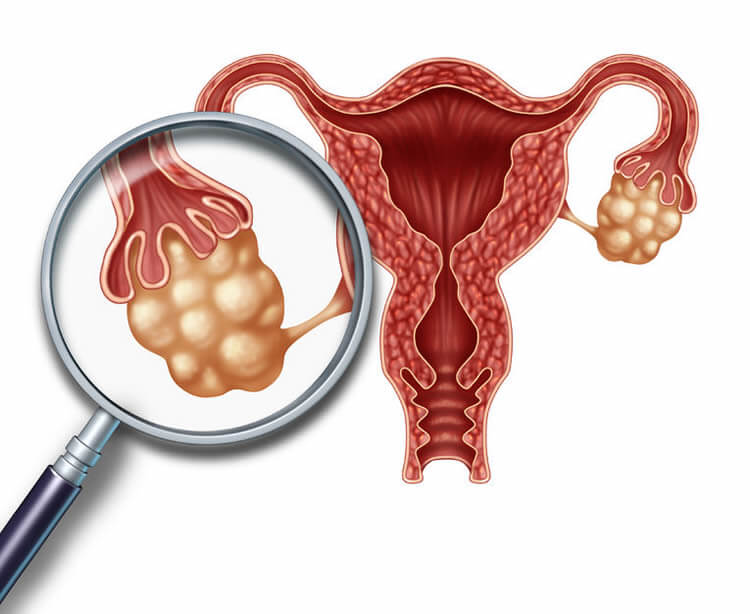
What is Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)?
Polycystic Ovary
Syndrome (PCOS) is a common endocrine disorder affecting many women. It is
characterized by the presence of multiple cysts on one or both ovaries.
What Causes PCOS?
The exact cause is
unknown, but the following factors may contribute:
- Elevated insulin levels in the blood
- Genetic predisposition
- High androgen (male hormone) levels
- Lifestyle factors such as smoking and
sedentary behavior
Symptoms of PCOS
- Irregular menstrual cycles
- Hair thinning or hair loss
- Difficulty maintaining or losing weight
- Acne or skin breakouts
Complications of
PCOS
- Insulin resistance or type 2 diabetes
- Weight gain
- High blood pressure
- Elevated blood lipids (cholesterol and
triglycerides)
PCOS Treatment
While doctors may
prescribe medications, lifestyle modification is essential for managing
PCOS. This includes:
- Engaging in regular physical activity
- Following a low glycemic index (GI)
diet
- Losing excess weight, if applicable
- Quitting smoking
Tips to Increase
Physical Activity
- Use stairs instead of elevators
- Park farther away and walk to your
destination
- Engage in family or group activities like
biking or sports
- Try home-based exercises like jumping rope
What is the
Glycemic Index (GI)?
The glycemic index
measures how quickly a food raises blood sugar levels after eating. Foods are
categorized into three groups:
- Low GI (≤55)
- Medium GI (56–69)
- High GI (≥70)
Examples of Foods
by Glycemic Index
|
Low GI Foods |
Medium GI Foods |
High GI Foods |
|
Quinoa |
Couscous |
White bread |
|
Pasta |
Apricots |
Bagels |
|
Milk |
Rye bread |
Potatoes |
|
Oats |
Pineapple |
Watermelon |
|
Oranges |
Ice cream |
Sweetened cereals |
|
Bulgur wheat |
Grapes |
Honey |
|
Bran bread |
Brown rice |
Soda |
|
Lentils |
Raisins |
Instant rice &
pasta |
|
Boiled sweet potato |
Beets |
Parsnips |
|
Cooked beans |
Oat cakes |
— |
- Faghfoori, Zeinab & Fazelian, Siavash & Shadnoush, Mahdi & Goodarzi, Reza. (2017). Nutritional management in women with polycystic ovary syndrome: A review study. Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews. 11 Suppl 1. 10.1016/j.dsx.2017.03.030.
- https://www.rubadiet.com/%d8%a7%d9%84%d9%85%d8%a4%d8%b4%d8%b1-%d8%a7%d9%84%d8%ac%d9%84%d8%a7%d9%8a%d8%b3%d9%8a%d9%85%d9%8a/
